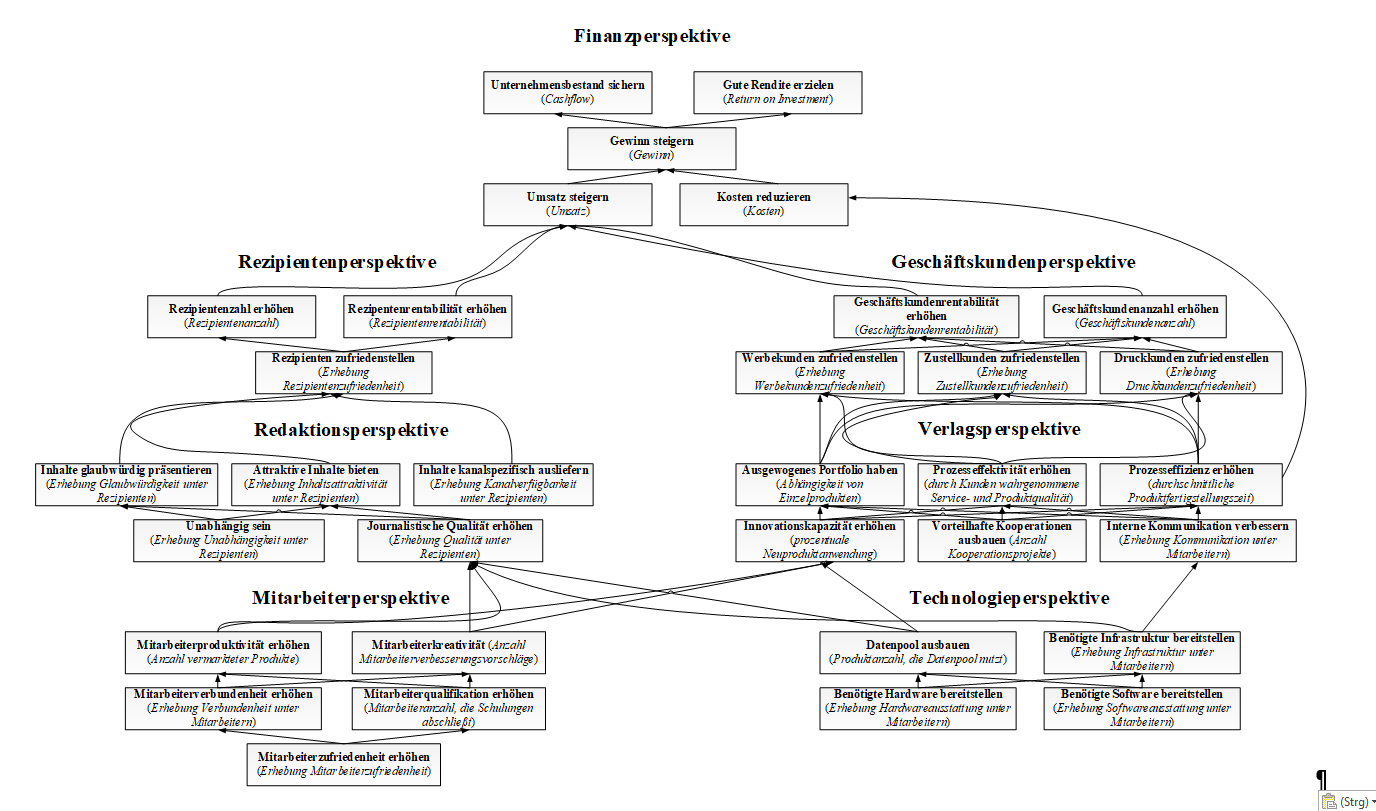
Designing a Media-Specific Balanced Scorecard by Applying Value-Focused Thinking
The Balanced Scorecard (Kaplan and Norton 1992) is one of the five management tools used most often and has been implemented by nearly 40 percent of the companies (Rigby and Bilodeau 2013). Yet, there is no theoretically sound approach for developing a balanced scorecard. Value-focused thinking is a decision-making philosophy that fits perfectly to Balanced Scorecard creation. It provides methods and techniques for the identification and structuring of objectives that are suitable to systematically derive a scorecard from a means-ends network. However, such a means-ends network is often too complex for enduring use in strategic management. By adapting the network’s structure to the Balanced Scorecard’s layout, the profound and clear set of derived objectives and their measures provide a reasonable basis for applying methods of multi-criteria decision-making in an organization. In a case study, we develop a media-specific Balanced Scorecard to provide media decision-makers with a model that takes characteristics of media management into account and that helps to manage their company successfully.
Die Entwicklung einer Balanced Scorecard mit Value-Focused Thinking am Beispiel eines Medienunternehmens
This paper describes an innovative procedure to develop a sophisticated Balanced Scorecard using tools and methods of Value-focused Thinking. This procedure is illustrated for a medium-sized media company.
Developing and Validating the Multidimensional Proactive Decision-Making Scale
On the basis of an extensive interdisciplinary literature review proactive decision-making (PDM) is conceptualised as a multidimensional concept. We conduct five studies with over 4,000 participants from various countries for developing and validating a theoretically consistent and psychometrically sound scale of PDM.
The PDM concept is developed and appropriate items are derived from literature. Six dimensions are conceptualised: the four proactive cognitive skills ‘systematic identification of objectives’, ‘systematic search for information’, ‘systematic identification of alternatives’, and ‘using a ‘decision radar’’, and the two proactive personality traits ‘showing initiative’ and ‘striving for improvement’. Using principal component factor analysis and subsequent item analysis as well as confirmatory factor analysis, six conceptually distinct dimensional factors are identified and tested acceptably reliable and valid.
Our results are remarkably similar for individuals who are decision-makers, decision analysts, both or none of both with different levels of experience. There is strong evidence that individuals with high scores in a PDM factor, e.g. proactive cognitive skills or personality traits, show a significantly higher decision satisfaction. Thus, the PDM scale can be used in future research to analyse other concepts. Furthermore, the scale can be applied, e.g. by staff teams to work on OR problems effectively or to inform a decision analyst about the decision behaviour in an organisation.
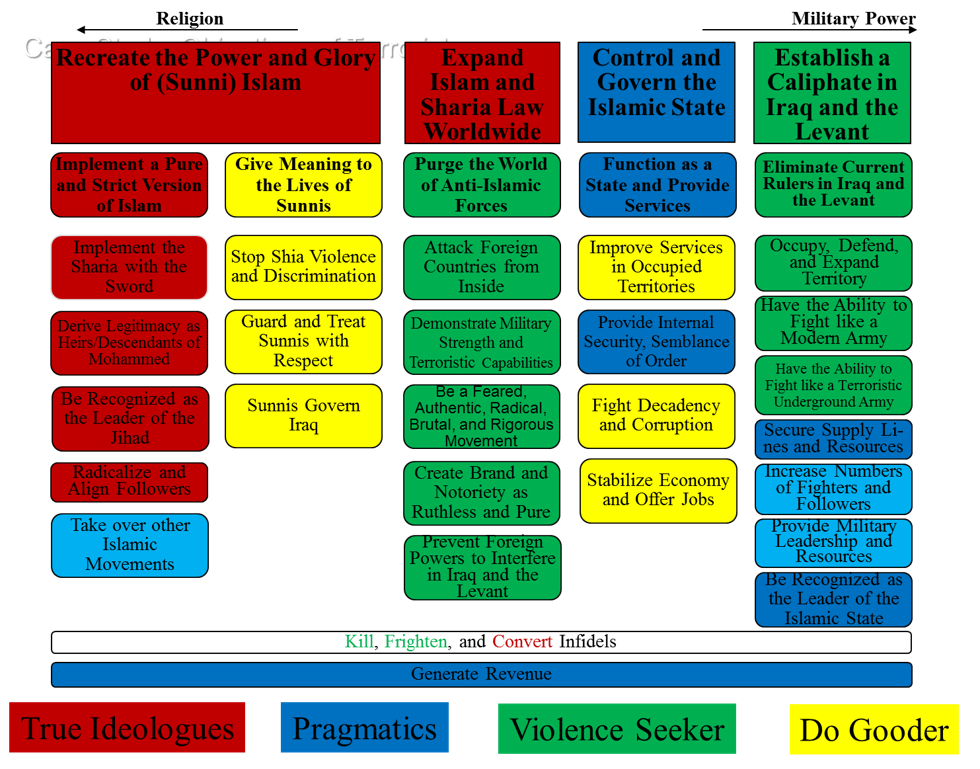
Identifying and Structuring the Objectives of the Islamic State of Iraq and The Levant (Isil) and its Followers
This study addressed three questions: 1. What are the objectives of the leaders of ISIL? 2. What are the objectives of the followers of ISIL? 3. How are the two sets of objectives related? To answer these questions we analyzed the transcripts of interviews and presentations of 59 subject matter experts (SMEs) and conducted a separate analysis of speeches of ISIL leaders and selected Internet sources. In both efforts we identified and structured the strategic, fundamental, and means objectives of ISIL and its followers.
The results indicate that ISIL’s leaders pursue four strategic objectives: Establish a Caliphate in Iraq and the Levant, Control and Govern the Caliphate, Expand Islam and Sharia Law Worldwide, and Recreate the Power and Glory of (Sunni) Islam. The followers’ objectives can be partitioned into three strategic objectives: Humanitarian Fulfillment, Religious Fulfillment and Personal Fulfillment.
The objectives identified from the SME interviews were similar to those identified from ISIL leaders’ statements and the Internet. However, the Internet search revealed many more personal objectives of ISIL followers. The results further indicate that ISIL’s leadership objectives are closely aligned with those of its followers. There also is a sharp contrast between the objectives of ISIL and those of Al Qaeda, particularly ISIL’s emphasis on occupying and controlling territories in Iraq and Syria vs. Al Qaeda’s focus on worldwide jihad.
Die Ziele des Islamischen Staats: Neue Studie zu den Führungspersonen des IS und seinen Anhängern
What does the Islamic State want? Dr. Johannes Siebert at the University of Bayreuth and U.S. researchers at the University of Southern California (USC) have systematically analyzed the IS’s objectives for the first time. The study was recently published in the renowned INFORMS journal Decision Analysis.
Deciding without tunnel vision – How the creative search for alternatives pays off
“There is no alternative!” was how British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher justified her economic and social policy reform program in the late 1970s. This slogan was soon caricatured in the media as the “TINA” principle. But do decisions without alternatives even exist? And what does their supposed lack of alternatives say about their quality? Recent studies resulting from a close collaboration between Bayreuth economist Dr. Johannes Siebert and U.S. decision theorist Prof. Dr. Ralph L. Keeney show: It is precisely when people look for different alternatives in a creative and goal-oriented way that the quality of their decisions increases. The two scientists present their results in the renowned journal “Operations Research”.
Creating More and Better Alternatives for Decisions Using Objectives
The quality of alternatives is crucial for making good decisions. This research, based on five empirical studies of important personally relevant decisions, examines the ability of decision makers to create alternatives for their important decisions and the effectiveness of different stimuli for improving this ability. For decisions for which the full set of potentially desirable alternatives is not readily apparent, our first study indicates that decision makers identify less than half of their alternatives and that the average quality of the overlooked alternatives is the same as those identified. Four other studies provide insight about how to use objectives to stimulate the alternative-creation process of decision makers and confirm with high significance that such use enhances both the number and quality of created alternatives. Using results of the studies, practical guidelines to create alternatives for important decisions are presented.
Industrie 4.0 und Controlling: Erste Konturen Zeichnen sich ab
Veröffentlichung Schlüchtermann, Jörg; Siebert, Johannes U. “Industrie 4.0 und Controlling: Erste Konturen zeichnen sich ab“. Schwerpunktheft „Controlling & Industrie 4.0“ der Controlling:Zeitschrift für erfolgsorientierte Unternehmenssteuerung, August/September 2015, 461-465. DOI: 10.15358/0935-0381-2015-8-9-461 This paper discusses the economic potentials of Industry 4.0, its interaction with Big Data, and provides implications for companies in general and for management control in particular.
Constructing a comprehensive strategic objectives network for an Energy Supplier
Germany is facing a huge disruptive change in its energy system. The speed of the transition from the fossil fuel and nuclear energy age to the renewable energies had been tremendously accelerated after Fukushima and the government´s decision to phase out of nuclear energy in the next 10 years. Therefore, traditional German utilities must make far-reaching decisions for ensuring long-term competitiveness. For that purpose, they need to define the future strategy and to agree on the right steps for its implementation. In the following 20 years decentralized renewable energy solutions, cost intensive offshore wind parks and the decommissioning of centralized conventional power plants have to be planned and realized. However, like in other industries, there is the tendency to deal with various decision problems isolated from each other without focusing on the big picture. Thereby it is often only vague defined what and how should be achieved. Furthermore, the search…